
© 1998 Steven L. Jacques, Scott A. Prahl
Oregon Graduate Institute
 |
ECE532 Biomedical Optics © 1998 Steven L. Jacques, Scott A. Prahl Oregon Graduate Institute |
The light scattered by a tissue has interacted with the
ultrastructure of the tissue. Tissue ultrastructure extends from
membranes to membrane aggregates to collagen fibers to nuclei to cells.
Photons are most strongly scattered by those structures whose size
matches the photon wavelength.
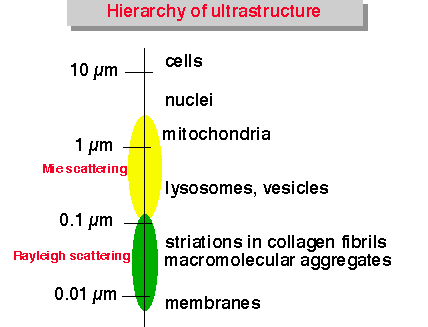
Scattering of light by structures on the same size scale as the photon wavelength is described by Mie theory. Scattering of light by structures much smaller than the photon wavelength is called the Rayleigh limit of Mie scattering, or simply Rayleigh scattering. The figure designates the size range of tissue ultrastructure which affects visible and infrared light by Mie and Rayleigh scattering.
Here are some examples of structures which scatter light (click on figure to expand):

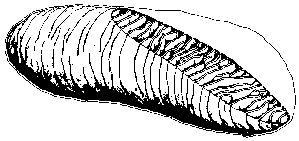
Mitochondria are intracellular organelles about 1 µm in length
(variable) which are composed of many folded internal lipid membranes
called cristae, as shown in the electron micrograph at left. The basic
lipid bilayer membrane is about 9 nm in width. The refractive index
mismatch between lipid and the surrounding aqueous medium causes strong
scattering of light. Folding of lipid membranes presents larger size
lipid structures which affect longer wavelengths of light. The density
of lipid/water interfaces within the mitochondria make them especially
strong scatterers of light.
(Drawing and micrographs from A. L. Lehninger,
"Biochemistry", Worth Publishers, 1970.)
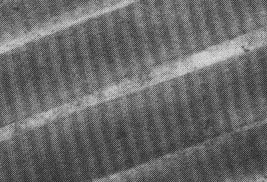
Collagen fibers (about 2-3 µm in diameter) are composed of
bundles of smaller collagen fibrils about 0.3 µm in
diameter (variable), as shown in the electron micrograph at left. Mie
scattering from collagen fibers dominates scattering in the infrared
wavelength range.
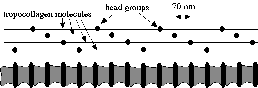
On the ultrastructural level, fibrils are composed of entwined tropocollagen molecules. The fibrils present a banded pattern of striations with 70-nm periodicity due to the staggered alignment of the tropocollagen molecules which each have an electron-dense head group that appears dark in the electron micrograph. The periodic fluctuations in refractive index on this ultrastructureal level appear to contribute a Rayleigh scattering component that dominates the visible and ultraviolet wavelength ranges.