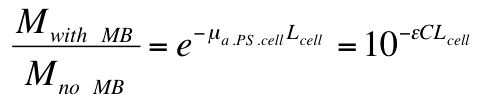
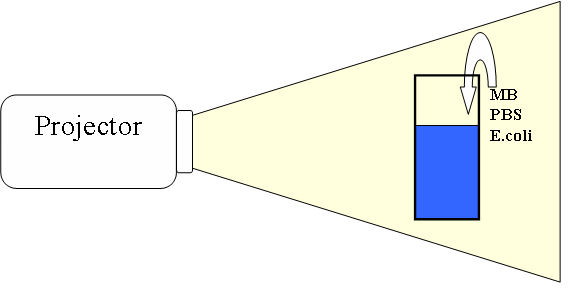
This figure shows the setup of PDI experiment. A cuvette with pure water was added MB, PBS and E.coli cells, the details are shown below. The solution was left and then irradiated with white light from a slide projector.
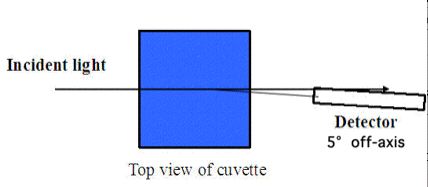
This figure shows the transmission experiment to measure the MB concentration inside the cuvette. The light source is collimated white light beam and the detector of spectrometer has a small angle (about 5 °) with the incident light to avoid the light which does not interact with any cells.
A sample of 103 cells of E. coli-MB solution was acquired at each time point during the PDI process, at 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 180, 300, 450, 600 and 900 seconds. The sampled cells were cultured on a nutrient plate @37°C for 8 hours. The number of colonies was counted. Inactivation was defined as survival = 10-2 (in other words, 10 CFU surviving out of the 1000 CFU plated).
Absorption of light by MB generated singlet oxygen to attack the E. coli cell. Since the diffusion of singlet oxygen was very limited, only the MB inside or adherent to the cells was effective for PDI. MB was added to 1 mL of solution (final concentration = 0.001 mg/mL) which contained E. coli cells (105 CFU/mL) in a cuvette and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes without light. A portion of the MB was taken up by the cells. The E. coli-MB solution was centrifuged and the cells resuspended in 1 mL of water. Collimated white light was delivered to the cuvette. Light at 630 nm scattered at ~3 degrees off-axis was measured, which yielded a total photon path length through E. coli interior equaled approximately 1 cell diameter. The chances for multiple interaction with E. coli cells was small.
The ratio of measurements, with MB (Mwith MB) and without MB (Mno MB), was calculated:
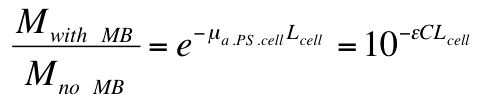
The pathlength L is the path through a single cell, and approximately equals the diameter of an E. coli cell (Lcell = 2 μm). The concentration C in the above equation is the concentration of MB within each E. coli cell. Rearranging the above equation yields the value of C to be 0.122 mg/mL, which is a 122-fold increase over the 0.001 mg/mL concentration of MB in the solution. The E. coli cells have concentrated the MB. The final value of the MB absorption coefficient, μa.PS.cell, was 35 cm-1. The final concentration of MB in the cells, C, was 381 μM.