
© 1998 Steven L. Jacques, Scott A. Prahl
Oregon Graduate Institute

| ECE532 Biomedical Optics © 1998 Steven L. Jacques, Scott A. Prahl Oregon Graduate Institute |
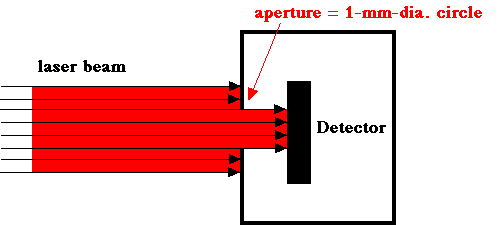
An aperture is essentially a hole through which light can pass to reach some detection system.
Consider a collimated laser beam delivering a power of 1 W to a circular 1-mm-diameter aperture. The laser beam has a Gaussian beam profile with a 1/e2 radius wo = 0.5 mm. A detector sits behind the aperture and is greater than 1 mm in diameter.
What is the power collected by the aperture?
The irradiance E [W/cm2] of the Gaussian beam profile is described as a function of the radial position r [cm] from the central axis of the beam:
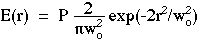
where
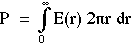
The aperture presents a collection radius a = 0.5 mm. In general, the amount of power collected, Pcollected, by an aperture with radius a is:
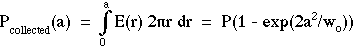
For our case,
next | Collect | Radiometry